Answer:
For this given plane monochromatic electromagnetic wave with wavelength λ=598 nm, the wavenumber is
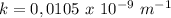 .
.
Step-by-step explanation:
For a plane electromagnetic wave we have that the electrical and magnetic field are:
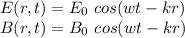
In this case we have the data for the magnetic field. We are told that the magnetic field in a plane electromagnetic wave with wavelength λ=598 nm, propagating in a vacuum in the z direction (
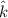 ) is described by
) is described by
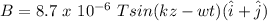
(
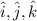 are the unit vectors in the x,y,z directions respectively)
are the unit vectors in the x,y,z directions respectively)
The wavenumber k is a measure of the spatial frequency of the wave, is defined as the number of radians per unit distance:
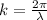
where λ is the wavelength
So we get that
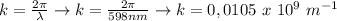
The wavenumber is
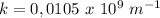 .
.