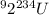Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
Plutonium is a heavy atom with a high mass to neutron ration (N/Z). Atoms with Z > 50 and an M/Z ratio of 1.25 or above tend to decay in a nuclear fission in which they release alpha particle, also known as a helium nucleus.
Let's say that our products are alpha particle and some unknown nucleus X with a mass of M and an atomic number of Z. Then our nuclear decay equation becomes:
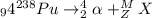
In order to identif X, we need to apply the law of mass conservation first. That is, the mass of reactants should be equal to the mass of products:
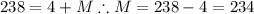
Similarly, apply the law of charge conservation to identify Z:
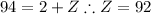
Z = 92 corresponds to uranium, meaning X is: