Answer:
E. 1/16
Step-by-step explanation:
In a duplicate dominant epistasis, when one locus presents a dominant genotype and the other presents a recessive genotype, the dominant one hides the effective of the recessive gene. Therefore, a recessive phenotype will only be observed when both genes are recessive homozygous (aabb).
Assuming a doubly-heterozygous mating (AaBb x AaBb), the probability that both genes are recessive homozygous is:
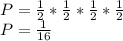
1/16 of offspring are expected to show the recessive phenotype.