Answer:
w = 7.89 10⁻² rad/s
Step-by-step explanation:
We will solve this exercise with the conservation of the annular moment, let's write it in two moments
Initial. With the insect in the center
L₀ = I w₀
End with the bug on the edge
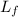 = I w +
= I w +
 w
w
The moments of inertia are
For a rod
I = 1/3 M L²
For the insect, taken as a particle
I = m L²
The system is formed by the rod and the insect, this is isolated, therefore the external torque is zero and the angular momentum is conserved
L₀ =
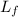
I w₀ = I w +
 w
w
w = I / (I +
 ) w₀
) w₀
w = I / (I + m L²) w₀
Let's calculate
w = 1.43 10⁻³ / (1.43 10⁻³ + 5 10⁻³ 0.620²)² 0.185
w = 1.43 10⁻³ / 3.352 10³ 0.185
w = 7.89 10⁻² rad/s