Answer:
242.862 grams is the theoretical yield of the reaction.
Nitrogen gas is a limiting reactant.
Hydrogen gas is an excessive reactant.
Step-by-step explanation:
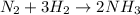
Moles of nitrogen gas =
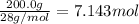
Moles of hydrogen gas =
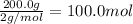
According to reaction, 1 mole of nitrogen reacts with 3 moles of hydrogen gas.
Then 7.413 moles of nitrogen will react with:
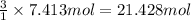 of hydrogen gas.
of hydrogen gas.
Moles of hydrogen that will react with 7.143 moles of nitrogen gas is less than the moles of hydrogen gas we have. This means that hydrogen gas is in an excessive reactant.
Nitrogen gas is in less amount hence limiting reactant.
Since, moles of nitrogen are in limiting amount so the amount of ammonia formed will depend upon moles of nitrogen gas.
According to reaction ,1 mole of nitrogen gives 2 moles of ammonia.
Then 7.143 moles of nitrogen will give:
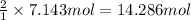 of ammonia
of ammonia
Mass of 14.286 moles of ammonia :
= 14.286 mol × 17 g/mol= 242.862 g
242.862 grams is the theoretical yield of the reaction.