Answer:
(a)
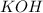 acts as base.
acts as base.
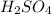 acts as acid.
acts as acid.
(b)
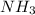 acts as base.
acts as base.
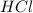 acts as acid.
acts as acid.
Step-by-step explanation:
Arrhenius theory:-
The Arrhenius theory was introduced introduced by Swedish scientist named Svante Arrhenius in 1887.
According to the theory, acids are the substances which dissociate in the aqueous medium to produce electrically charged atoms ( may be molecule). Out of these species furnished, one must be a proton or the hydrogen ion,
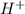 .
.
Base are the substances which dissociate in the aqueous medium to produce electrically charged atoms ( may be molecule). Out of these species furnished, one must be a hydroxide ion,
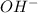 .
.
Thus, according to the reaction:-
(a)
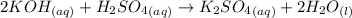
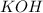 dissociates as:-
dissociates as:-
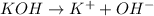 and hence, acts as base.
and hence, acts as base.
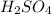 dissociates as:-
dissociates as:-
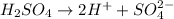 and hence, acts as acid.
and hence, acts as acid.
(b)
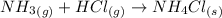
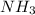 dissociates as:-
dissociates as:-
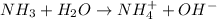 and hence, acts as base.
and hence, acts as base.
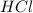 dissociates as:-
dissociates as:-
 and hence, acts as acid.
and hence, acts as acid.