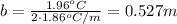Answer:
(a) 0.575 m;
(b) 0.527 m
Step-by-step explanation:
Let's use the freezing point depression law in each of these cases.
(a) According to the law:
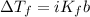
Rearrange the equation for molality, b:
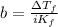
NaCl is an ionic substance, 1 mole of it dissociates into 2 moles of ions, sodium ion and chloride ion, this means the van 't Hoff factor i = 2.
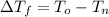
Here:
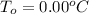 is the initial freezing point of water,
is the initial freezing point of water,
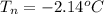 is the final freezing point of water.
is the final freezing point of water.
For water:
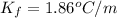
Applying the equation
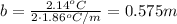
(b) Applying the same equation for the same salt and the same conditions, except a new freezing point, we would expect to obtain: