Answer: 54.4 kJ/mol
Step-by-step explanation:
First we have to calculate the moles of HCl and NaOH.
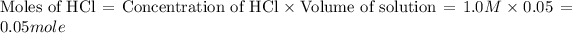
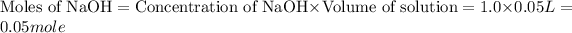
The balanced chemical reaction will be,

From the balanced reaction we conclude that,
As, 1 mole of HCl neutralizes by 1 mole of NaOH
So, 0.05 mole of HCl neutralizes by 0.05 mole of NaOH
Thus, the number of neutralized moles = 0.05 mole
Now we have to calculate the mass of water:
As we know that the density of water is 1 g/ml. So, the mass of water will be:
The volume of water =
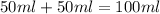
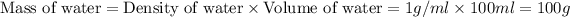
Now we have to calculate the heat absorbed during the reaction.
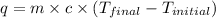
where,
q = heat absorbed = ?
 = specific heat of water =
= specific heat of water =
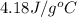
m = mass of water = 100 g
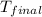 = final temperature of water =
= final temperature of water =
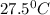
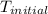 = initial temperature of metal =
= initial temperature of metal =
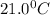
Now put all the given values in the above formula, we get:
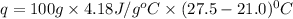
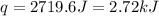
Thus, the heat released during the neutralization = 2.72 KJ
Now we have to calculate the enthalpy of neutralization per mole of
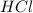 :
:
0.05 moles of
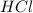 releases heat = 2.72 KJ
releases heat = 2.72 KJ
1 mole of
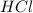 releases heat =
releases heat =
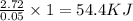
Thus the enthalpy change for the reaction in kJ per mol of HCl is 54.4 kJ