Answer: The redox reactions that occur spontaneously are Reaction W and Reaction Z.
Step-by-step explanation:
For the reaction to be spontaneous, the Gibbs free energy of the reaction must come out to be negative.
Relationship between standard Gibbs free energy and standard electrode potential follows:
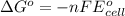
For a reaction to be spontaneous, the standard electrode potential must be positive.
To calculate the
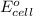 of the reaction, we use the equation:
of the reaction, we use the equation:
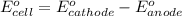 .......(1)
.......(1)
Substance getting oxidized always act as anode and the one getting reduced always act as cathode.
The chemical reaction follows:
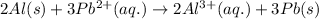
We know that:
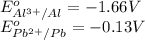
Calculating the
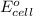 using equation 1, we get:
using equation 1, we get:
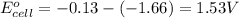
As, the standard electrode potential is coming out to be positive. So, the reaction is spontaneous.
The chemical reaction follows:
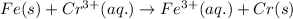
We know that:
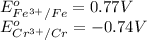
Calculating the
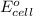 using equation 1, we get:
using equation 1, we get:

As, the standard electrode potential is coming out to be negative. So, the reaction is not spontaneous.
The chemical reaction follows:
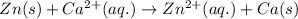
We know that:
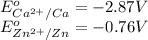
Calculating the
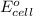 using equation 1, we get:
using equation 1, we get:
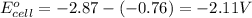
As, the standard electrode potential is coming out to be negative. So, the reaction is not spontaneous.
The chemical reaction follows:
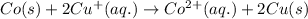
We know that:
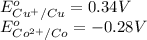
Calculating the
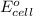 using equation 1, we get:
using equation 1, we get:
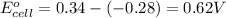
As, the standard electrode potential is coming out to be positive. So, the reaction is spontaneous.
Hence, the redox reactions that occur spontaneously are Reaction W and Reaction Z.