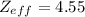Answer:
The effective nuclear charge for a valence electron in oxygen atom:
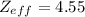
Step-by-step explanation:
Effective nuclear charge
![[Z_(eff)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/tcb0bgqwfqfwfgyo1ya5xgnufn9bjfxjhe.png) is the net nuclear charge experienced by the electron in a given atom. It is always less than the actual charge of the nucleus [Z], due to shielding by electrons in the inner shells.
is the net nuclear charge experienced by the electron in a given atom. It is always less than the actual charge of the nucleus [Z], due to shielding by electrons in the inner shells.
It is equal to the difference between the actual nuclear charge or the atomic number (Z) and the shielding constant (s).
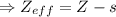
For an oxygen atom-
Electron configuration: (1s²) (2s² 2p⁴)
The atomic number (actual nuclear charge): Z = 8
The shielding constant (s) for a valence electron can be calculated by using the Slater's rules:
⇒ s = 5 × 0.35 + 2 × 0.85 = 1.75 + 1.7 = 3.45
Therefore, the effective nuclear charge for a valence electron in oxygen atom is:
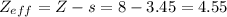
Therefore, the effective nuclear charge for a valence electron in oxygen atom: