Answer:
The individual who scores 123 on test A has a higher zscore, so he has the higher IQ.
Explanation:
Problems of normally distributed samples can be solved using the z-score formula.
In a set with mean
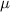 and standard deviation
and standard deviation
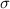 , the zscore of a measure X is given by:
, the zscore of a measure X is given by:
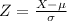
The Z-score measures how many standard deviations the measure is from the mean. After finding the Z-score, we look at the z-score table and find the p-value associated with this z-score. This p-value is the probability that the value of the measure is smaller than X, that is, the percentile of X. Subtracting 1 by the pvalue, we get the probability that the value of the measure is greater than X.
In this problem, we have that:
The individual with the higher IQ is the one with the higher z-score. So
Test A has a mean of 100 and a standard deviation of 13. An individual who scores 123 on Test A.
So
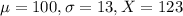
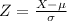
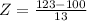
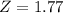
Test B has a mean of 100 and a standard deviation of 18. An individual who scores 121 on Test B.
So
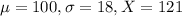
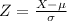
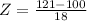
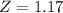
The individual who scores 123 on test A has a higher zscore, so he has the higher IQ.