Answer : The value of
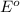 and
and
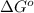 is, 0.034 V and -3.281 kJ/mol
is, 0.034 V and -3.281 kJ/mol
Explanation :
From the given half reactions we conclude that, the cathode will be with more reduction potential and anode will have low reduction potential.
First we have to calculate the standard electrode potential of the cell.
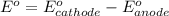
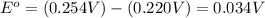
Relationship between standard Gibbs free energy and standard electrode potential follows:
Formula used :
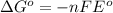
where,
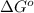 = Gibbs free energy = ?
= Gibbs free energy = ?
n = number of electrons = 1
F = Faraday constant = 96500 C/mole
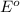 = standard e.m.f of cell = 0.034 V
= standard e.m.f of cell = 0.034 V
Now put all the given values in this formula, we get the Gibbs free energy.
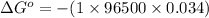
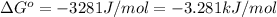
Therefore, the value of
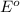 and
and
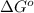 is, 0.034 V and -3.281 kJ/mol
is, 0.034 V and -3.281 kJ/mol