Answer:
a) I = 270.18 Kg*m/s
b) F = -3216.42N
Step-by-step explanation:
a) We know that:
I =
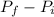
Where I is the impulse,
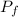 is the final momentum and
is the final momentum and
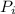 the initial momentum.
the initial momentum.
so:
I =
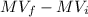
where M is the mass,
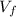 is the final velocity and
is the final velocity and
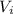 is the initial velocity.
is the initial velocity.
First we have to find the
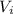 . So, using the conservation of energy.
. So, using the conservation of energy.
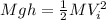
where g the gravity and h the altitude. Replacing values, we get:
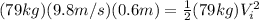
solving for
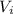 :
:
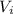 = 3.42 m/s
= 3.42 m/s
Now, replacing in the previus equation:
I =
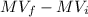
I =
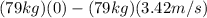
I = -270.18 Kg*m/s
The impulse is negative becuase it is upward.
b) We know that:
Ft = I
where F is the force, t the time and I the impulse.
so, replacing values and solving for F, we get:
F(0.084s) = -270.18 Kg*m/s
F = -3216.42N
The force is negative becuase it is upward.