Answer:
468449163762.0812 W
Step-by-step explanation:
m = Mass =

V = Volume =
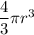
r = Distance of sphere from isotropic point source of light = 0.5 m
R = Radius of sphere = 2 mm
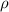 = Density = 19 g/cm³
= Density = 19 g/cm³
c = Speed of light =
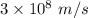
A = Area =
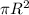
I = Intensity =
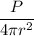
g = Acceleration due to gravity = 9.81 m/s²
Force due to radiation is given by
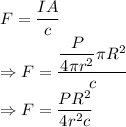
According to the question
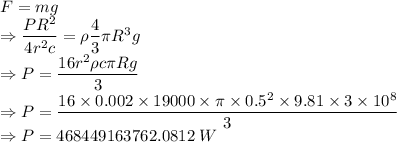
The power required of the light source is 468449163762.0812 W