Answer:
3.80 atm
Step-by-step explanation:
First of all, ammonium nitrite decomposes to produce nitrogen gas and liquid water at the given room temperature:
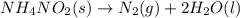
Notice that the solid decomposes fully and produces the same number of moles of nitrogen:
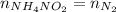
Find moles of ammonium nitrite multiplying its molarity by its volume:
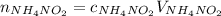
Express moles of nitrogen in terms of the ideal gas law:
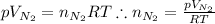
Substitute the two expressions above into the molar ratio equation:
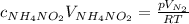
Solve for the pressure:
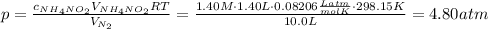
Notice that here R is the ideal gas law constant and we've converted the temperature into the absolute temperature:
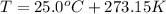 .
.
Therefore, the overall final pressure would be 4.80 atm. Since initially we had air in the vessel at standard conditions (1.00 atm), the change in pressure would be 4.80 atm - 1.00 atm = 3.80 atm.