Answer:
The reactant that has the atom that gets oxidized
Step-by-step explanation:
A redox reaction is a reaction in which one substance is oxidized and one is reduced. The easiest way to remember the patterns of any redox reaction is to follow a simple abbreviation: OILRIG.
This acronym stands for: oxidation is loss, reduction is gain (of electrons). Therefore, if a substance is oxidized, then it loses electrons. If a substance is reduced, it gains electrons.
Let's take a look at the following example:
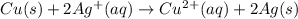
Notice that copper loses two electrons, as it becomes positively charged:
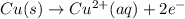
Since electrons are on the right-hand side, it means we produce them (they are lost). Hence, copper in this equation is oxidized. Similarly:
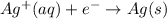
Now, silver cation gains electrons to become solid silver, neutrally charged, meaning it is reduced.
In terms of an oxidizing/reducing agents, the thought process is opposite: in an oxidation process, we have a reducing agent, hence, Cu (s) is our reducing agent. In a reduction process, we have an oxidizing agent, hence, silver cation is our oxidizing agent.
Both reducing and oxidizing agents are reactants.
Therefore, reducing agent is a reactant that has the atom that gets oxidized.