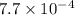Answer:
The value of equilibrium constant for reverse reaction is
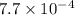
Step-by-step explanation:
The given chemical equation follows:
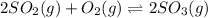
The equilibrium constant for the above equation is
 .
.
We need to calculate the equilibrium constant for the reverse equation of above chemical equation, which is:
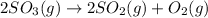
The equilibrium constant for the reverse reaction will be the reciprocal of the initial reaction.
If the equation is multiplied by a factor of '1/2', the equilibrium constant of the reverse reaction will be the square root of the equilibrium constant of initial reaction.
So,
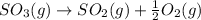
The value of equilibrium constant for half reverse reaction is:
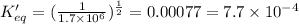
Hence, the value of equilibrium constant for reverse reaction is