Answer:
Oxygen, bromine, iron, helium
Step-by-step explanation:
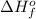 is defined as the standard enthalpy of formation. By definition, the standard enthalpy of formation is equal to 0 kJ/mol for the substances in their standard states, that is, at room temperature and 1 atm pressure.
is defined as the standard enthalpy of formation. By definition, the standard enthalpy of formation is equal to 0 kJ/mol for the substances in their standard states, that is, at room temperature and 1 atm pressure.
Simply speaking, looking at the substances given, we need to understand whether their states agree with what we expect to see at standard conditions (e. g., sodium is a metal, fluorine is a gas, bromine is a liquid at standard conditions). Those are substances consisting of just one type of atoms.
- Firstly, oxygen is a gas at standard conditions and it is diatomic, so its
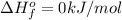 .
.
- Although nitrogen is a gas at standard conditions, it is diatomic, so
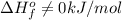 .
.
- Water is a liquid at standard conditions, however, it consists of two types of atoms, hydrogen and oxygen, so
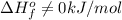 .
. - Bromine is a liquid at standard conditions, so
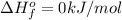 .
. - Iron is a solid at standard conditions, it's a metal, so
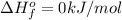 .
. - Helium is a gas at standard conditions, it belongs to noble gases, so
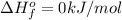 .
. - Sulfur is a solid at room conditions, however, the conformation it has is
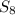 and not
and not
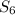 , so
, so
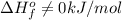 .
.