Answer:
(a) 0.032 nm
(b) 39,235 eV
(c) 70,267.8 eV
Step-by-step explanation:
(a) The energy of a photon can be calculated using:
E = hc/λ equation (1)
where:
h = 4.13*10^-15 eV.s
c = 3*10^8 m/s
λ = 0.024*10^-9 m
Thus:
E = (4.13*10^-15)*(3*10^8)/0.024*10^-9 = 51,625 eV
Then we calculate 76% of this estimated energy and determine the new wavelength:
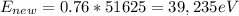
Using equation (1) to determine the new wavelength:
λ
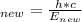
λ
 = (4.13*10^-15)*(3*10^8)/39235 = 3.15*10^-11 m = 0.032 nm
= (4.13*10^-15)*(3*10^8)/39235 = 3.15*10^-11 m = 0.032 nm
(b) As calculated in part (a), the maximum x-ray energy this machine can produce is
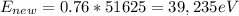
(c) The energy of a Ka x-ray photon can be estimated using:
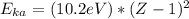
where Z is the atomic number = 84.
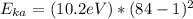 = 70,267.8 eV
= 70,267.8 eV