Answer:
401.17 K is the minimum temperature at which the reaction will become spontaneous under standard state conditions.
Step-by-step explanation:
The expression for the standard change in free energy is:
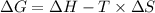
Where,
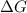 is the change in the Gibbs free energy.
is the change in the Gibbs free energy.
T is the absolute temperature. (T in kelvins)
 is the enthalpy change of the reaction.
is the enthalpy change of the reaction.
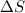 is the change in entropy.
is the change in entropy.
Given at:-
Temperature = 25.0 °C
The conversion of T( °C) to T(K) is shown below:
T(K) = T( °C) + 273.15
So,
T₁ = (25.0 + 273.15) K = 298.15 K
 = 128.9 kJ/mol
= 128.9 kJ/mol
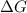 = 33.1 kJ/mol
= 33.1 kJ/mol
Applying in the above equation, we get as:-
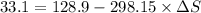
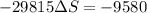
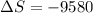 = 0.32131 kJ/Kmol
= 0.32131 kJ/Kmol
So, For reaction to be spontaneous,
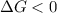
Thus, For minimum temperature:-
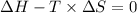
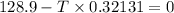
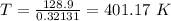
Hence, 401.17 K is the minimum temperature at which the reaction will become spontaneous under standard state conditions.