Answer:
Double the current
Step-by-step explanation:
The energy delivered by the heater is related to the current by the following relation:
E=
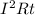
let R * t = k ( ∴ R and t both are constant)
so E= k
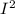
Now let:
E2= k I₂^2
E2= 4E
⇒ k I₂^2= 4* k
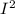
Cancel same terms on both sides.
I₂^2= 4*
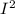
taking square-root on both sides.
√I₂^2 = √4* I^2
⇒I₂= 2I
If we double the current the energy delivered each minute be 4E.