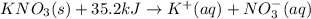Answer:
Equation correctly showing the heat of solution
Step-by-step explanation:
Mass of aqueous solution = m = 100 g
Specific heat of solution = c = 4.18 J/gºC
Change in temperature =
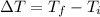
ΔT = 21.6ºC - 30.0ºC = -8.4ºC
Heat lost by the solution = Q
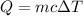
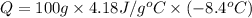
Q = -3,511.2 J ≈ -3.51 kJ
Heat absorbed by potassium nitrate when solution in formed; Q'
Q' = -Q = 3.51 kJ
Moles of potassium nitrate , n=
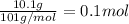
The heat of solution =
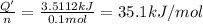
So, the equation correctly showing the heat of solution