Answer:
-V(X + c) = V(X) + c
Explanation:
Using the propierties of the variance:
- The variance of a constant is zero:
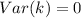
Where k is an arbitrary constant. So:
-V(c) = 0 is true.
- If all values are scaled by a constant, the variance is scaled by the square of that constant:
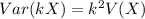
Where k is an arbitrary constant. Therefore:
-V(cX) = c2 V(X) is true.
- Variance is invariant with respect to changes in a location parameter. That is, if a constant is added to all values of the variable, the variance is unchanged:
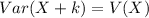
Where k is an arbitrary constant. Hence:
-V(X + c) = V(X) + c is not true.