Answer:
1.175 V
Step-by-step explanation:
We are given that
Work function of the material=
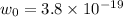 J
J
Wavelength of light=
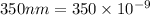 m
m
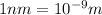
Energy of photon=Work function+Kinetic energy of electron
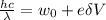
Where
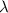 =Wavelength of light
=Wavelength of light
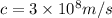 =Speed of light
=Speed of light
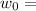 Work function
Work function
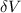 =Small voltage
=Small voltage
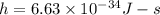 =Plank's constant
=Plank's constant

Substitute the values then we get
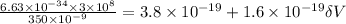
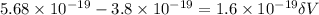
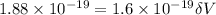
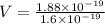
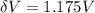
Hence, the lowest voltage needed between the cathode and the anode to stop any electrons ejected from the cathode from reaching the anode=1.175 V