Answer:
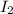 = 0.0050 M
= 0.0050 M
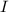 = 0.0155 M
= 0.0155 M
Step-by-step explanation:
Initial moles of
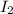 = 0.072 mole
= 0.072 mole
Volume of container = 3.9 L
Initial concentration of
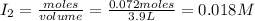
The given balanced equilibrium reaction is,
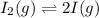
Initial conc. 0.018 M 0
At eqm. conc. (0.018-x) M (2x) M
The expression for equilibrium constant for this reaction will be,
![K_c=([I]^2)/([I_2])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/physics/college/yi6r5e3c2s905d5l2ape3hg6vlqhb5hupz.png)
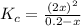
we are given :
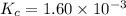
Now put all the given values in this expression, we get :
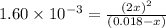
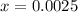
So, the concentrations for the components at equilibrium are:
![[I]=2* x=2* 0.0025=0.0050](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/physics/college/85gg6tlakhfoqegeed7wi8knhatsqeqb5g.png)
![[I_2]=0.018-x=0.018-0.0025=0.0155](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/physics/college/uy1yoz28xxehqrcwv2uhy0jyj39w2gmg1r.png)
Hence, concentrations of
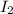 and
and
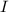 are 0.0050 M ad 0.0155 M respectively.
are 0.0050 M ad 0.0155 M respectively.