Answer: The heat released for the given process is -1892 kJ
Step-by-step explanation:
The processes involved in the given problem are:
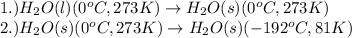
Pressure is taken as constant.
To calculate the amount of heat released at same temperature, we use the equation:
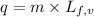 ......(1)
......(1)
where,
q = amount of heat released = ?
m = mass of water/ice
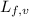 = latent heat of fusion or vaporization
= latent heat of fusion or vaporization
To calculate the amount of heat released at different temperature, we use the equation:
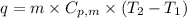 .......(1)
.......(1)
where,
q = amount of heat released = ?
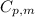 = specific heat capacity of medium
= specific heat capacity of medium
m = mass of water/ice
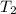 = final temperature
= final temperature
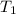 = initial temperature
= initial temperature
Calculating the heat absorbed for each process:
Converting the latent heat of fusion in J/kg, we use the conversion factor:
1 kJ = 1000 J
So,
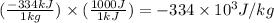
We are given:
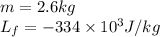
Putting values in equation 1, we get:
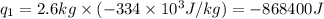
We are given:
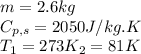
Putting values in equation 2, we get:
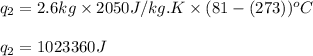
Total heat absorbed =
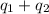
Total heat absorbed =
![[-868400+(-1023360)]J=-1891760J=-1891.76kJ\approx -1892kJ](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/ow6qb5sopz548kl7apsj8hu5zyamki2zmc.png)
Hence, the heat released for the given process is -1892 kJ