Answer:
![PV_(m) = RT[1 + (b-(a)/(RT))(1)/(V_(m) ) + (b^(2) )/(V^(2) _(m) ) + ...]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/pdsi6mx3m73g0h22wrxo6od0mc8g2u6qis.png)
B = b -a/RT
C = b^2
a = 1.263 atm*L^2/mol^2
b = 0.03464 L/mol
Step-by-step explanation:
In the given question, we need to express the van der Waals equation of state as a virial expansion in powers of 1/Vm and obtain expressions for B and C in terms of the parameters a and b. Therefore:
Using the van deer Waals equation of state:
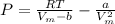
With further simplification, we have:
![P = RT[(1)/(V_(m)-b ) - (a)/(RTV_(m) ^(2) )]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/m61bes57tf0zf4av3k0mfo6qmaxybyxgps.png)
Then, we have:
![P = (RT)/(V_(m) ) [(1)/(1-(b)/(V_(m) ) ) - (a)/(RTV_(m) )]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/ahcy560818g8ck635ix16817jhu22amtsh.png)
Therefore,
![PV_(m) = RT[(1-(b)/(V_(m) )) ^(-1) - (a)/(RTV_(m) )]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/1xbhxdv3dsdeev154el2bhmh69nv0j9pj9.png)
Using the expansion:
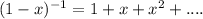
Therefore,
![PV_(m) = RT[1+(b)/(V_(m) )+(b^(2) )/(V_(m) ^(2) ) + ... -(a)/(RTV_(m) )]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/sixgil6u9p6mnqi3zfatc7p8wma35bhm7u.png)
Thus:
![PV_(m) = RT[1 + (b-(a)/(RT))(1)/(V_(m) ) + (b^(2) )/(V^(2) _(m) ) + ...]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/pdsi6mx3m73g0h22wrxo6od0mc8g2u6qis.png) equation (1)
equation (1)
Using the virial equation of state:
![P = RT[(1)/(V_(m) )+ (B)/(V_(m) ^(2))+(C)/(V_(m) ^(3) )+ ...]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/tir3seh5e44vne0nfoblg70wyflbcjrcyu.png)
Thus:
![PV_(m) = RT[1+ (B)/(V_(m) )+ (C)/(V_(m) ^(2) ) + ...]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/hqhyapn94ud9tkbuqcsvtnv99x6gp2lwn7.png) equation (2)
equation (2)
Comparing equations (1) and (2), we have:
B = b -a/RT
C = b^2
Using the measurements on argon gave B = −21.7 cm3 mol−1 and C = 1200 cm6 mol−2 for the virial coefficients at 273 K.
![b = √(C) = √(1200) = 34.64[tex]cm^(3)/mol](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/ll4zv7somw7y0sxg1mbu52mor6fru7cp9e.png) [/tex] = 0.03464 L/mol
[/tex] = 0.03464 L/mol
a = (b-B)*RT = (34.64+21.7)*(1L/1000cm^3)*(0.0821)*(273) = 1.263 atm*L^2/mol^2