Answer : The enthalpy of the given reaction will be, -1048.6 kJ
Explanation :
According to Hess’s law of constant heat summation, the heat absorbed or evolved in a given chemical equation is the same whether the process occurs in one step or several steps.
The main reaction is:
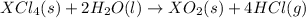
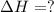
The intermediate balanced chemical reactions are:
(1)
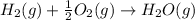
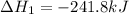
(2)
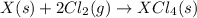
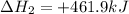
(3)
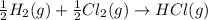

(4)
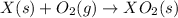
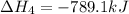
(5)
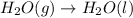

Now reversing reaction 2, multiplying reaction 3 by 4, reversing reaction 1 and multiplying by 2, reversing reaction 5 and multiplying by 2 and then adding all the equations, we get :
(1)
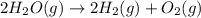
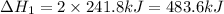
(2)
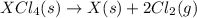

(3)
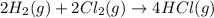
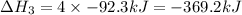
(4)
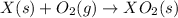
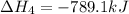
(5)
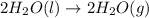
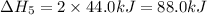
The expression for enthalpy of main reaction will be:
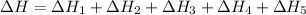
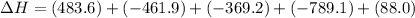
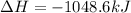
Therefore, the enthalpy of the given reaction will be, -1048.6 kJ