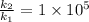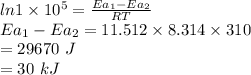Answer:
30 kJ
Step-by-step explanation:
Arrhenius equation is given by:
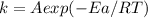
Here, k is rate constant, A is Pre-exponential factor, Ea is activation energy and T is temperature.
taking natural log of both side
ln k = ln A - Ea/RT
In Arrhenius equation, A, R and T are constant.
Therefore,
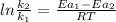
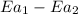 is the lowering in activation energy by enzyme,
is the lowering in activation energy by enzyme,
R = 8.314 J/mol.K
T = 37°C + 273.15 = 310 K