Answer:
T² ∝ R³
Step-by-step explanation:
Given data,
The period of revolution of the planet around the sun, T
The mean distance of the planet from the sun, R
According to the III law of Kepler, " Law of Periods' states that the square of the orbital period to go around the sun once is directly proportional to the cube of the mean distance between the sun and the planet.
T² ∝ R³
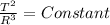
From the above equation it is clear that T² varies directly as the R³.