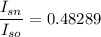Answer:
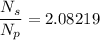
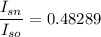
Step-by-step explanation:
V denotes voltage
I denotes current
p denotes primary
s denotes secondary
o denotes old
n denotes new
N denotes number of turns
For transformers we have the following relation
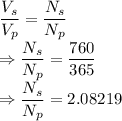
The required ratio is
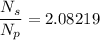
For current
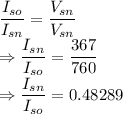
The required ratio is