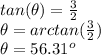Answer:
Final distance from the origin: 10.82 km. the vector points as shown in the attached image.
Angle with respect to the east:
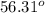
Step-by-step explanation:
Please refer to the attached image. The cyclist's trip is indicated with the green arrows (9 km to the north followed by 6 km to the east.
So his final position is at the tip of this last vector, and indicated by the orange vector drawn form the point where the trip starts to the cyclist's final location.
We observe that this orange vector is in fact the hypotenuse of a right angle triangle, and we can estimate the distance from the origin by the Pythagorean theorem:
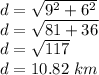
Notice that this is NOT the actual number of km that the cyclist pedaled to reach the final point.
Now, to find the value of the angle
 , we need to use trigonometry, and in particular the tangent function gives us the ratio between the side of the triangle "opposite" to the angle, divided the side "adjacent" to the angle:
, we need to use trigonometry, and in particular the tangent function gives us the ratio between the side of the triangle "opposite" to the angle, divided the side "adjacent" to the angle:
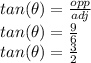
Now we can find the value of the angle by using the arctan function: