Answer:
A. 14 min
B . 0.995 M
Step-by-step explanation:
A.
Using integrated rate law for first order kinetics as:
![[A_t]=[A_0]e^(-kt)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/wgh5hifj7f12vitsa51kophgqrxxcfit2c.png)
Where,
![[A_t]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/wbj92t0z4axifcyqa24z3ary269op2iva8.png) is the concentration at time t
is the concentration at time t
![[A_0]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/izynxfnwyud2ghdog9l8ny0mhzwshbud6r.png) is the initial concentration
is the initial concentration
Given:
The final concentration is dropped to 6.25 % of the initial concentration. SO,
![\frac {[A_t]}{[A_0]}](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/rdky51ah6e4fo6vkh0t5pkijdlldqfq8xn.png) = 0.0625
= 0.0625
k =
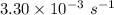
So,
![\frac {[A_t]}{[A_0]}=e^(-k* t)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/tixyocmkbxlfsradct604h51a1nrscvy5b.png)
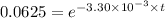
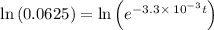
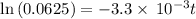
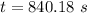
Also, 1 s = 1/60 minutes.
So,
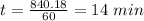
14 minutes it takes for the concentration of the reactant to drop to 6.25% of the original concentration.
B.
(a) Half life expression for second order kinetic is:
![t_(1/2)=(1)/(k[A_o])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/dtbcugt1e5y67l6hck0xrmf78wr0xtmewi.png)
Where,
![[A_o]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/38eb24kf04xqy5t88y9g0vzh3m04r4nqgg.png) is the initial concentration = ?
is the initial concentration = ?
k is the rate constant =
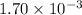 M⁻¹s⁻¹
M⁻¹s⁻¹
Half life = 296 s
So,
![296=(1)/(1.70* 10^(-3)* [A_o])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/3wpmbt6s0zj6any0fr3n057eqctzburkjl.png)
![296=(1000)/(1.7[A_o])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/vtvgfyy7xeub4gdy5yst80q4jsw2lmihxo.png)
![[A_o]=(1250)/(629)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/ldkon7o384deas0s6cwi82o60nsg4dnuo1.png)
![[A_o]=1.99\ M](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/qhulp0mr8yelvg2kd8f4ikzhi83kjvt5jj.png)
Half life is the time at which the concentration of the reactant reduced to half. So, concentration remains =
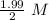 = 0.995 M
= 0.995 M