Step-by-step explanation:
Using Gibbs Helmholtz equation:
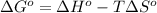
- ΔG° = negative (spontaneous)
- ΔG° = positive (non spontaneous)
a)
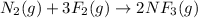
ΔH°=-249 kJ = -249000 J , ΔS°=-278J/K
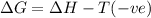
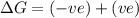
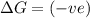 (at low Temperature)
(at low Temperature)
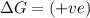 (at high Temperature)
(at high Temperature)
Spontaneous at low Temperature , Non-spontaneous at high Temperature;
b)

ΔH°=460kJ = 460,000 J, ΔS°=-275 J/K
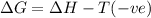
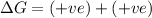
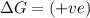
Non spontaneous at all temperatures.
(c)
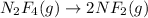
ΔH°= 85kJ 85,000 J , ΔS°= 198J/K
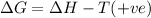
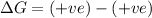
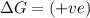 (at low temperature)
(at low temperature)
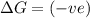 (at high temperature)
(at high temperature)
Spontaneous at high Temperature non-spontaneous at low temperature.