Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
mass, m = 2 kg
radius, r = 3.1 m
L(t) = 10 - 3.5 t
(a)
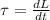
So, differentiate angular momentum with respect to time
τ = - 3.5 Nm
As the particle is rotating clockwise, so the angular velocity is downward and the angular momentum decreases so torque is upward.
(b) moment of inertia, I = m R²
I = 2 x 3.1 x 3.1 = 19.22 kgm^2
L = I x ω
where, ω is the angular velocity
ω = (10 - 3.5 t) / 19.22
ω = 0.520 - 0.182 t
So, by comparison A = 0.520 rad/s
B = - 0.182 rad/s²