Answer:
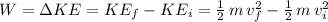
Step-by-step explanation:
The Work-Kinetic Energy Theorem states that the work done on a particle of mass "m", equals the particle's change in Kinetic Energy (final Kinetic Energy of the particle "
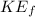 " minus the initial Kinetic energy of the particle "
" minus the initial Kinetic energy of the particle "
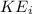 "), and it is expressed as:
"), and it is expressed as:
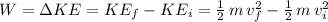
where we have used the explicit form of the KE of a particle of mass m and velocity
 . Of course,
. Of course,
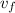 stands for the final velocity of the particle, and
stands for the final velocity of the particle, and
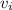 for the particle's initial velocity.
for the particle's initial velocity.