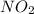Answer:
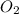 and
and
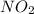
Step-by-step explanation:
For a given system at constant temperature, the number of moles of gas present in the system is proportional to the product of the system pressure and volume. Therefore, we have:
NO: 6 L * 0.7 atm = 4.2 L*atm
O: 1.5 L* 2.5 atm = 3.75 L*atm
For the given system based on a balanced chemical equation:
2.70 L*atm of nitric oxide reacts with (2.7/2) 1.35 L*atm of oxygen. This shows that there is more oxygen gas in the system than nitric oxide. Thus nitric oxide is the limiting reactant.
At the end of the experiment:
All the nitirc oxide has been used up, i.e.
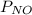 = 0
= 0
For the product: 2.70 L*atm NO produced 2.70 L*atm
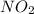
The total volume of the system after the stopcock is opened = 6+1.5 = 7.5 L
The partial pressure of
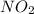 = (2.70 L*atm
= (2.70 L*atm
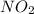 ) / (7.5 L) = 0.36 atm
) / (7.5 L) = 0.36 atm
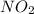
Similarly for oxygen gas:
3.75 L*atm - 1.35 L*atm = 2.40 L*atm oxygen gas remaining
Partial pressure of oxygen is:
2.40 L*atm / 7.5 L = 0.32 atm
Thus, the gases present at the end of the experiment are
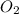 and
and