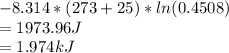Answer:
(i)The mole fractions are :
(ii)
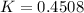
(iii)ΔG = 1.974kJ
Step-by-step explanation:
The given equation is :
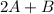 ⇄
⇄
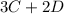
Let
 be the number of moles dissociated per mole of
be the number of moles dissociated per mole of
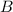
Thus ,
The initial number of moles of :
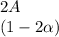 +
+
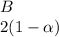 ⇄
⇄
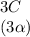 +
+
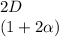
And finally the number of moles of
![C[tex] is 0.9</p><p>Thus ,</p><p>[tex]3\alpha=0.9\\\alpha=0.3[tex]</p><p><em><strong>The final number of moles of:</strong></em></p><ul><li><em><strong>[tex]A = 1-2\alpha=1-2*0.3=0.4mol[tex] </strong></em></li></ul><ul><li><em><strong>[tex]B=2(1-\alpha)=2(1-0.3)=1.4mol[tex]</strong></em></li></ul><ul><li><em><strong>[tex]D=1+2\alpha=1+2*0.3=1.6mol[tex]</strong></em></li></ul><p>Thus , total number of moles are : 0.4+1.4+0.9+1.6=4.3</p><p><strong>(i)The mole fractions are : </strong></p><ul><li><strong>[tex]A=(0.4)/(4.3) \\=0.0930](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/681p84f2nll96fc36ddnx42xza1jiuvu3l.png)
(ii)
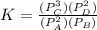
Where ,
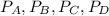 are the partial pressures of A,B,C,D respectively.
are the partial pressures of A,B,C,D respectively.
Total pressure = 1 bar .
∴
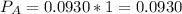
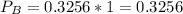
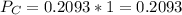
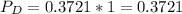
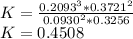
(iii)
Δ
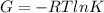
ΔG =