Step-by-step explanation:
The given reaction is as follows.
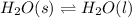
Hence, using standard values heat of fusion will be calculated as follows.
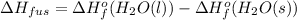
= -285.8 kJ/mol - (-291.8 kJ/mol)
= 6 kJ/mol
Therefore, heat released from beverage will be calculated as follows.
q =
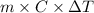
=
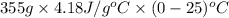
= -37133 J
or, = -37.133 kJ (as 1 J = 0.001 kJ)
Now, heat gained by ice = - heat released by the beverage
= - (-37.133 kJ)
= 37.133 kJ
Therefore, calculate the mass of ice as follows.
Mass of ice =
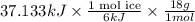
= 111.40 g
Thus, we can conclude that mass of ice is 111.40 g.