The unique identity of amino acid is that each amino acid is bonded to each central atom known as R-group.
Step-by-step explanation:
Amino acids are nothing but a basic structure which has a central atom called the "alpha carbon atom". This
 carbon atom is bonded to an "amino group" (
carbon atom is bonded to an "amino group" (
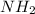 ), a "carboxyl group" (COOH) or a "hydrogen atom".
), a "carboxyl group" (COOH) or a "hydrogen atom".
There are totally "20 types" of amino acids having a central atom bonded from the R-group. For example: When the R-group is hydrogen, then the amino acid is named glycine. Similarly, if it is attached to methyl group, then the amino acid is alanine. This makes the amino acids unique.