Answer : The equilibrium concentration of NO is, 0.0092 M.
Solution :
First we have to calculate the concentration of NO.
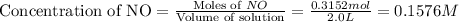
The given equilibrium reaction is,
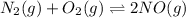
Initially conc. 0 0 0.1576
At eqm. (x) (x) (0.1576-2x)
The expression of
 will be,
will be,
![K_c=([NO]^2)/([N_2][O_2])](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/h97e3v9ia7fb0kvxd3enqoq711mg7wqk69.png)
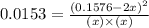
By solving the term, we get:
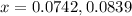
Neglecting the 0.0839 value of x because it can not be more than initial value.
Thus, the value of 'x' will be, 0.0742 M
Now we have to calculate the equilibrium concentration of NO.
Equilibrium concentration of NO = (0.1576-2x) = [0.1576-2(0.0742)] = 0.0092 M
Therefore, the equilibrium concentration of NO is, 0.0092 M.