Answer:
493.02 nm is the longest wavelength of light that will produce free chlorine atoms in solution.
Step-by-step explanation:
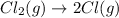 ,ΔH = 242.8 kJ/mol
,ΔH = 242.8 kJ/mol
Energy required to break 1 mole of Cl-Cl bond = 242.8 kJ
Energy required to break 1 Cl-Cl bond = E
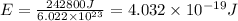
Energy related with the wavelength of light is given by Planck's equation:
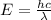
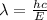
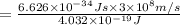
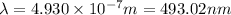
493.02 nm is the longest wavelength of light that will produce free chlorine atoms in solution.