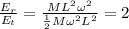Answer:
2
Step-by-step explanation:
The rotational kinetic energy of the dumbbell is:
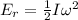
where I is the moments of inertia of the two point-like system
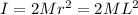
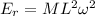
The translation kinetic energy is:
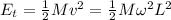
Therefore the ratio of the rotational kinetic energy to the translational (linear) kinetic energy is: