Answer:
E) -0.28 nC
Step-by-step explanation:
For using Gauss law
we calculate flux through whole cylinder.
- On curved part flux is zero
- On left par flux is =
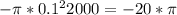
- On right par flux is =
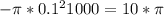
Total flux =-10
According to Gauss law
net flux along closed surface=
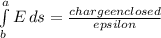 [epsilon =8.85 *
[epsilon =8.85 *
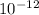 ]
]
10
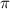 =
=
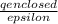
plug in the values
we get charge enclosed = -0.28 nC