To solve this problem we must use the concepts related to the Law of Malus and the intensity of light. The intensity of a linearly polarized beam of light, which passes through a perfect analyzer and vertical optical axis is equivalent to:
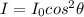
Where,
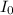 indicates the intensity of the light before passing through the polarizer
indicates the intensity of the light before passing through the polarizer
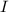 is the resulting intensity
is the resulting intensity
 indicates the angle between the axis of the analyzer and the polarization axis of the incident light.
indicates the angle between the axis of the analyzer and the polarization axis of the incident light.
Since the light has the same intensity after the first polarizer we approach the second intensity directly so
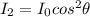
Our values are given as :
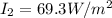
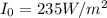
Therefore replacing and re-arrange to find the angle we have
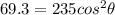
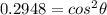
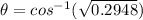
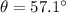
Therefore the angle of the second polarizer with respect to the first one is 57.1°