Answer:
506464 g/(cm*s^2)
Step-by-step explanation:
Atmospheric pressure is defined as the pressure caused by the mass of the gaseous atmosphere. With the use of mercury, atmospheric pressure = mercury density × acceleration due to gravity × height of column of mercury.
Normally, density of mercury = 13.6 ×density of water
If the density of water =
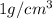
Thus, density of mercury =
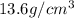
column of mercury = 760 mm = 76 cm
Acceleration due to gravity = 9.8
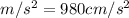
Therefore:
Atmospheric pressure = 13.6*76*980 = 1012928 g/(cm*s^2)
If a liquid with half the density of mercury is used, the atmospheric pressure will be equal to 1012928/2 = 506464 g/(cm*s^2)