Answer:
Approximately
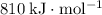 .
.
Assumption:
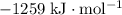 measures the enthalpy change of the reaction
measures the enthalpy change of the reaction
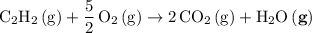 where the water is in its gaseous state (as "water vapor.")
where the water is in its gaseous state (as "water vapor.")
Step-by-step explanation:
The heat of combustion of a substance gives the enthalpy change when one mole of that substance reacts with excess oxygen.
Start by balancing the equation for the complete combustion of ethyne
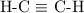 in oxygen
in oxygen
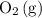 .
.
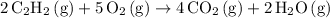 .
.
Set coefficient of
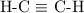 should be equal to one. Simply divide all coefficients by the coefficient of
should be equal to one. Simply divide all coefficients by the coefficient of
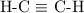 .
.
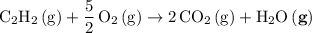 .
.
The enthalpy change of a reaction like this one is equal to
- The energy of bonds broken, minus
- The energy of bonds formed.
If the energy of bonds formed is greater than that of the bonds broken, the reaction would be exothermic and
 should be negative.
should be negative.
In each mole of this reaction, bonds broken include:
In each mole of this reaction, bonds formed include:
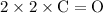 bonds (each
bonds (each
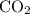 molecule contains two such bonds,) and
molecule contains two such bonds,) and
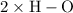 bonds.
bonds.
Hence
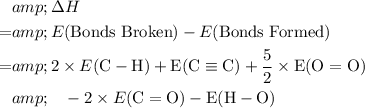 .
.
Rewrite the equation to isolate the unknown
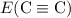 :
:
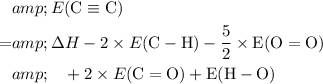 .
.
Look up the bond energy for these bonds (except for the unknown carbon-carbon triple bond)
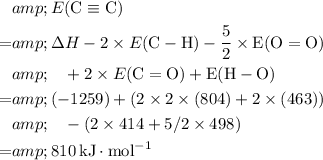 .
.