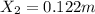Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
Using the law of the convervation of energy E:
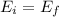
so:
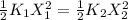
where
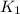 is the constant of the spring 1,
is the constant of the spring 1,
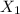 the compressed of the first spring,
the compressed of the first spring,
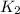 is the constant of the second spring and
is the constant of the second spring and
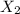 is the compressed of the second spring.
is the compressed of the second spring.
Replacing values, we get:
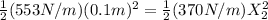
Solving for
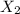 :
: