Answer:
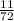
Explanation:
There are two shuffled decks each of which contains 12 cards.
we need to collect two cards, 1 card from each shuffled decks.
Taking the 1st suffled decks we need to drawn one. The probability of getting 6 from the 1st shuffled decks is
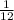 . In this scenario we need to find the probability of not getting 6 from the 2nd shuffled decks. The probability of not getting 6 is
. In this scenario we need to find the probability of not getting 6 from the 2nd shuffled decks. The probability of not getting 6 is
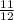 .
.
The case can also be vice-versa, that is we can get one 6 from the 2nd shuffled decks.
Hence the total probability is
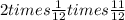 .
.
Theoritical probability refers to those outcomes which we suppose to be happen. Experimental probability means the outcomes which can come true if tried.
The given scenario is an example of Experimental probability, as it can also be true if tried.