Answer: The standard change in Gibbs free energy for the given reaction is 4.33 kJ/mol
Step-by-step explanation:
For the given chemical equation:
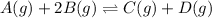
The expression of
 for the given reaction:
for the given reaction:
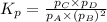
We are given:
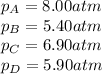
Putting values in above equation, we get:
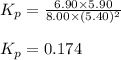
To calculate the standard Gibbs free energy, we use the relation:
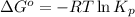
where,
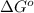 = standard Gibbs free energy
= standard Gibbs free energy
R = Gas constant =
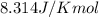
T = temperature =
![25^oC=[25+273]K=298K](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/physics/high-school/h3swi627jfkpg7vx7in8p5pe35bz1gwehq.png)
 = equilibrium constant in terms of partial pressure = 0.174
= equilibrium constant in terms of partial pressure = 0.174
Putting values in above equation, we get:
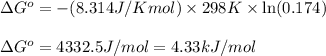
Hence, the standard change in Gibbs free energy for the given reaction is 4.33 kJ/mol